PS: This article is being continuously updated!
Color
-
LUT: A Look-Up Table (LUT) is mathematically precise way of taking specific RGB image values form a source image – and modifying them to new RGB values by changing the hue, saturation and brightness values of that source image. Link. There are several different types of LUTs available: calibration, transform, viewing, 1D and 3D.
1D LUT is called such because it is controlled by one value setting, and can be boiled down to a gamma curve preset, and most commonly find 1D LUTs that use the .lut extension. 3D LUT maps hue, saturation, and brightness to an individual axis, so that you have much more control over specific color values in your image. These are commonly found with .cube file extensions.
Image
-
Acutance: Sharpening: Image sharpness is a combination of two factors: resolution and acutance. The acutance tells how visually sharp the edges in the image are and there is no standard way of measuring it.
-
Vibrance: Colors can be adjusted for example by saturation and vibrance. Saturation means increasing the intensity of all colors of the image, which can result in oversaturation in certain colors and lead to loss of details in those areas. Oversaturated skin can look orange and unnatural. Vibrance is a more robust tool to adjust colors by only affecting the intensity of the colors that are not already well saturated. This gives the image a more natural like lighting.
Noise
- Guassian noise:
- salt and pepper noise:
Floyd–Steinberg dithering
The Floyd-Steinberg method is actually a dithering method. By dithering the color information of this pixel to other pixels in a certain way, the regional effect of the color can be better utilized.
Floyd–Steinberg dithering is the algorithm which convert gray image (256 level) to binary (0 or 1) image.
The algorithm achieves dithering using error diffusion, meaning it pushes (adds) the residual quantization error (quant_err = old_pix - new_pix) of a pixel onto its neighboring pixels, to be dealt with later. It spreads the debt out according to the distribution (shown as a map of the neighboring pixels):
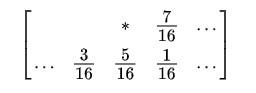
The pixel indicated with a star (*) indicates the pixel currently being scanned, and the blank pixels are the previously-scanned pixels. The algorithm scans the image from left to right, top to bottom, quantizing pixel values one by one.
Image Pyramid
Downsampling is any linear transformation of the form, which includes nearest, bilinear, bicubic, etc.
Gaussian Pyramid
Image pyramid is a pyramid structure for rapidly processing image in a smaller scale. (Down-sampling) It could be processed based on a 2x2 filtering or a 4x4 filtering. For 4x4 filtering, we create a 4x4 weight mask as [1 3 3 1] by [1; 3; 3; 1], in total 64.
The representation is based on 2 basic operations: 1. Smoothing and 2. Downsampling. Gaussian Pyramid needs Gaussian filtering before each down-sampling.
Example - Python(OpenCV):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
def gaussian(ori_image, down_times=5):
# 1:Add original image as 0 level
temp_gau = ori_image.copy()
gaussian_pyramid = [temp_gau]
for i in range(down_times):
# 2:Save 5 times down-sampling images to get a 6 levels gaussian pyramid
temp_gau = cv2.pyrDown(temp_gau)
gaussian_pyramid.append(temp_gau)
return gaussian_pyramid
Laplace Pyramid
Laplace pyramid is used for saved residual/difference image between original image and Up[downsampling(image)], which is usually used to restore the down sampling image with Gaussian pyramid.
Example - Python(OpenCV):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
def laplacian(gaussian_pyramid, up_times=5):
laplacian_pyramid = [gaussian_pyramid[-1]]
for i in range(up_times, 0, -1):
# i is [5,4,3,2,1,0] to get a 6 levels laplace pyramid
temp_pyrUp = cv2.pyrUp(gaussian_pyramid[i])
temp_lap = cv2.subtract(gaussian_pyramid[i-1], temp_pyrUp)
laplacian_pyramid.append(temp_lap)
return laplacian_pyramid
Block Matching
In image, the value of pixels is related to the value of surrounding pixels. The whole image could be divided into subimages as different size, normally including 4x4, 8x8 and 16x16.
DFT/FFT (Discrete/Fast Fourier Transform)
DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform)
Generally speaking, the DCT transform is actually a low-pass filter in the spatial domain. The Direct current (DC) information could be reserved, and Alternating current (AC) will be ignored.
FDCT and IDCT (Forward and Inverse Discrete Cosine Transforms)
对应专有名词的中文含义
- halo:
- flicker:
- maze:
- haze:
- Coma (optics): comatic aberration (彗形像差)